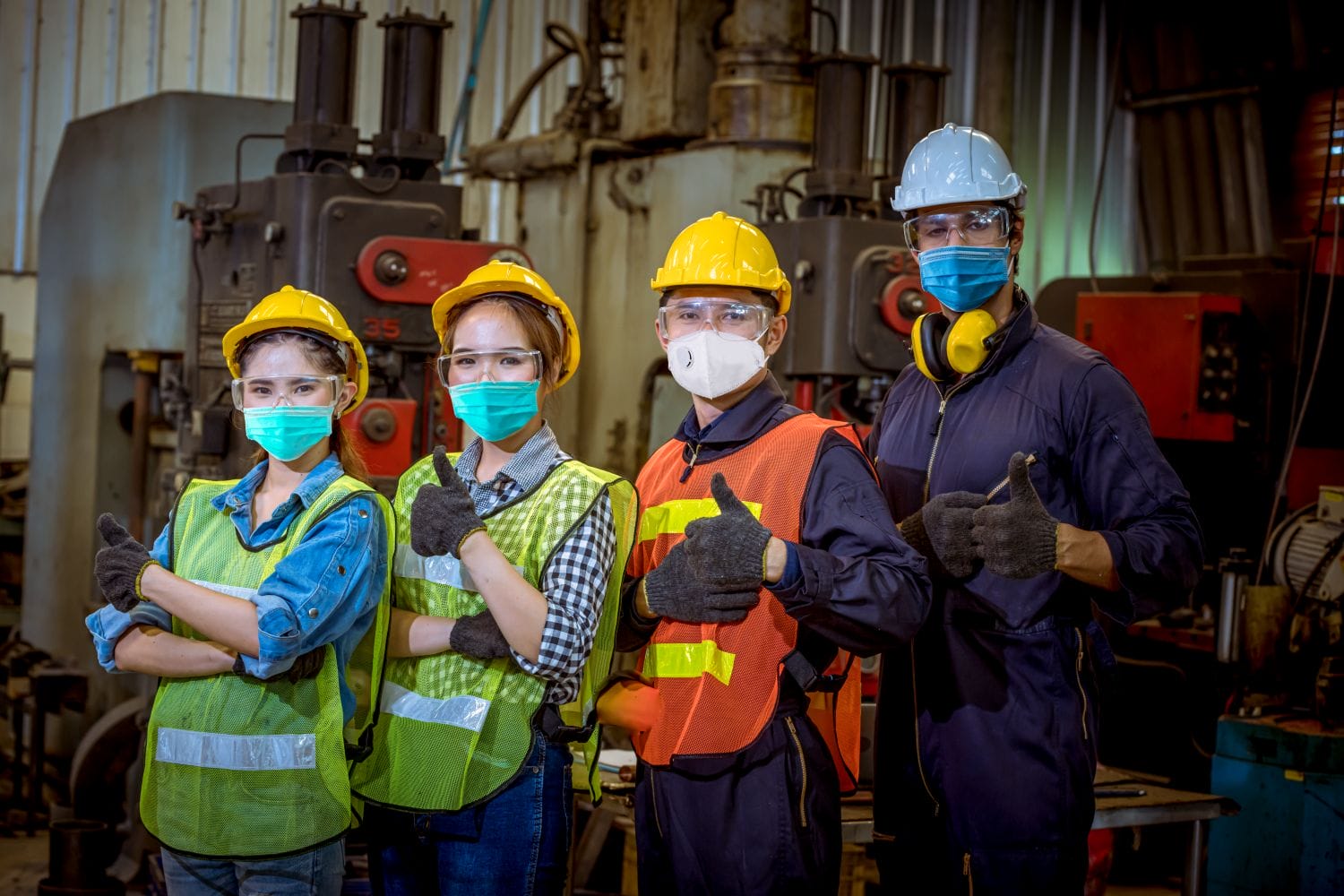
What are PPE Safety Certifications?
PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) safety certifications are formal approvals that ensure protective equipment meets specific safety, quality, and performance standards set by regulatory bodies and industry organizations. These certifications guarantee that PPE—such as gloves, masks, respirators, helmets, safety glasses, and protective clothing—provides adequate protection against hazards in the workplace. PPE certifications involve rigorous testing and evaluation processes to confirm that equipment can effectively protect workers from chemicals, biological agents, physical hazards, and other dangers present in various industries.
PPE safety certifications are critical for ensuring that protective equipment used in industries like healthcare, construction, manufacturing, and chemical processing meets the legal and safety requirements set by regulatory authorities such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health), the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), and international organizations like CE marking in Europe.
Why PPE Safety Certifications Matter in the Enterprise Environment
In industries where workers face high-risk hazards, PPE safety certifications provide assurance that the protective equipment meets the necessary safety standards to mitigate risks effectively. Certified PPE ensures that workers are equipped with gear that has been tested for durability, performance, and reliability, protecting them from injuries, illnesses, or fatalities that could result from exposure to hazardous materials or environments.
For employers, using certified PPE helps maintain compliance with workplace safety regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties, fines, and potential liabilities. Certified PPE also supports worker confidence and well-being, ensuring that they are adequately protected while performing high-risk tasks.
In addition to safeguarding workers, PPE safety certifications contribute to regulatory compliance, as many industries are required by law to use certified protective equipment. This is particularly important for industries that handle hazardous chemicals, infectious materials, or environments prone to physical hazards such as falling objects or airborne particles.
Key PPE Safety Certifications
Several regulatory bodies and organizations provide certifications for different types of PPE. Each certification focuses on specific types of protective equipment, ensuring they meet the safety standards for particular hazards. The following are some of the most recognized PPE safety certifications:
1. NIOSH Certification (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health)
- Purpose: NIOSH certifies respiratory protection equipment, including N95 respirators, to ensure they provide adequate protection against airborne particles, such as dust, fumes, and pathogens.
- Common Uses: Healthcare (for protection against airborne diseases like COVID-19), construction (protection from dust and particulates), chemical processing.
- Certification Process: NIOSH conducts performance testing to ensure respirators meet the minimum filtration efficiency and breathability requirements. NIOSH-certified respirators must filter out at least 95% of airborne particles.
2. OSHA Compliance (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
- Purpose: OSHA enforces safety standards for various types of PPE, requiring employers to provide certified equipment that protects workers from workplace hazards. OSHA references other standards, such as those from ANSI and NIOSH, for specific PPE.
- Common Uses: Construction, manufacturing, healthcare, chemical industries.
- Certification Process: OSHA requires that employers use PPE that meets the safety standards outlined in OSHA regulations, ensuring the equipment is effective against identified workplace hazards. OSHA does not directly certify PPE but mandates compliance with standards like ANSI, ASTM, and NIOSH.
3. CE Marking (Conformité Européenne)
- Purpose: CE marking indicates that PPE sold in the European Economic Area (EEA) meets the EU’s safety, health, and environmental protection standards. The PPE Regulation (EU) 2016/425 governs the design and manufacturing of PPE in Europe.
- Common Uses: Construction, healthcare, manufacturing, and other industries in Europe.
- Certification Process: PPE must be tested and approved by a notified body, and manufacturers must demonstrate that their equipment meets the safety standards outlined by the European Union before it can carry the CE mark.
4. ANSI (American National Standards Institute) Certification
- Purpose: ANSI sets voluntary safety and performance standards for a wide range of PPE, including helmets, safety glasses, protective footwear, and gloves.
- Common Uses: Construction, manufacturing, healthcare, laboratories.
- Certification Process: PPE certified to ANSI standards undergoes rigorous testing for impact resistance, durability, and other performance factors. Employers are often required to use ANSI-certified equipment to meet OSHA’s regulatory standards.
5. FDA Certification (Food and Drug Administration)
- Purpose: The FDA regulates medical-grade PPE, such as surgical masks, gowns, gloves, and face shields, to ensure that it is safe and effective for use in healthcare settings.
- Common Uses: Hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and other healthcare environments.
- Certification Process: The FDA assesses the safety and performance of medical PPE, ensuring that it meets specific standards for protection against infectious diseases and contaminants. FDA approval is mandatory for medical devices used in healthcare, including certain types of PPE.
6. NFPA Certification (National Fire Protection Association)
- Purpose: NFPA certification applies to flame-resistant clothing, protective gear, and equipment used in fire-prone environments, ensuring that it provides adequate protection against heat, flames, and other fire-related hazards.
- Common Uses: Firefighting, oil and gas, chemical processing, construction.
- Certification Process: PPE certified by the NFPA undergoes testing for fire resistance, heat protection, and durability. NFPA standards such as NFPA 2112 for flame-resistant clothing outline the performance requirements for PPE used in high-temperature environments.
7. ISO (International Organization for Standardization) Certification
- Purpose: ISO develops international standards for various types of PPE, including protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. ISO certification ensures that PPE meets global quality and safety benchmarks.
- Common Uses: Construction, manufacturing, chemical processing, and healthcare worldwide.
- Certification Process: ISO-certified PPE must undergo testing to meet the performance criteria set by specific ISO standards. ISO standards are widely recognized across industries and regions, ensuring consistent quality and safety.
8. ASTM International Certification
- Purpose: ASTM International develops standards for protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and helmets, to ensure they meet performance requirements for impact resistance, cut protection, and chemical resistance.
- Common Uses: Construction, healthcare, laboratories, manufacturing.
- Certification Process: PPE certified to ASTM standards is tested for performance factors such as chemical resistance, puncture resistance, and durability, depending on the specific equipment.
Benefits of PPE Safety Certifications
PPE safety certifications offer several key benefits, ensuring that protective equipment is reliable and effective in preventing workplace injuries or illnesses. These benefits include:
- Assured Protection: Certified PPE has been rigorously tested to meet specific safety standards, providing workers with the confidence that their equipment will protect them from identified hazards in their work environment.
- Regulatory Compliance: PPE safety certifications ensure that equipment meets the safety regulations set by OSHA, NIOSH, the FDA, CE marking, and other regulatory bodies. Using certified PPE helps businesses avoid fines, penalties, and legal liabilities resulting from non-compliance.
- Worker Confidence: Employees can trust that certified PPE provides reliable protection, enhancing their safety and well-being in hazardous work environments. This, in turn, can improve productivity and reduce anxiety in high-risk settings.
- Global Standards: Certifications like CE marking and ISO certification provide assurance that PPE meets international safety standards, allowing businesses to use certified equipment across different countries and industries with confidence.
- Quality Assurance: Certified PPE undergoes rigorous testing for durability, performance, and safety, ensuring that it offers long-term protection and quality. This helps reduce the need for frequent replacements, offering cost savings over time.
The Role of Enterprise Software in Managing PPE Certifications
Enterprise software solutions play a critical role in managing PPE safety certifications, helping organizations track and maintain compliance with regulatory standards. Key features of enterprise software for managing PPE certifications include:
- Certification Tracking: The software can track the certification status of all PPE, ensuring that the equipment being used in the workplace is certified and compliant with relevant safety standards.
- Compliance Monitoring: Enterprise software helps organizations monitor compliance with OSHA, NIOSH, FDA, and other regulatory requirements, ensuring that PPE meets safety standards and is being used correctly.
- Inventory Management: The software can manage PPE inventory, tracking when certifications expire and automatically flagging equipment that needs to be replaced or re-certified.
- Training and Certification Records: The software can maintain records of employee training on certified PPE, ensuring that workers are properly trained to use certified equipment in hazardous environments.
Conclusion
PPE safety certifications are essential for ensuring that protective equipment provides adequate protection against workplace hazards. Certifications from regulatory bodies like NIOSH, OSHA, FDA, CE, and ANSI ensure that PPE meets stringent safety standards, protecting workers from chemical exposure, infectious agents, physical injuries, and other risks. For businesses, using certified PPE not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also supports worker confidence and well-being. Enterprise software solutions further streamline the management of PPE certifications, ensuring compliance, safety, and efficiency in the workplace. By using certified PPE, organizations can minimize risks, maintain safety, and foster a culture of health and protection in high-risk environments.
« Back to Glossary Index