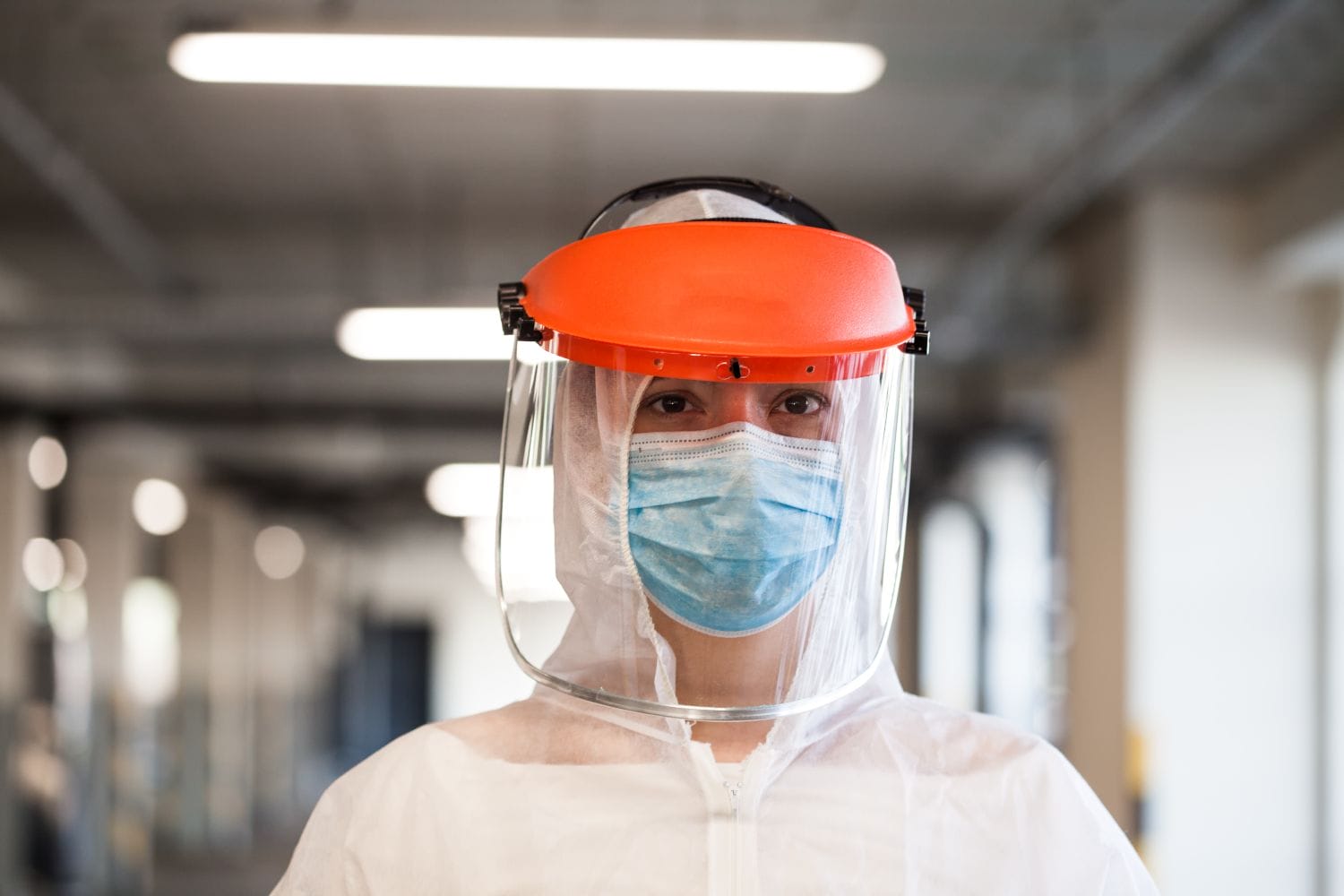
What is Contaminant Control?
Contaminant control is the process of preventing, managing, and reducing the spread of harmful substances, such as biological, chemical, or particulate contaminants, within a specific environment. In the context of the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) industry, contaminant control involves using protective gear, sanitation protocols, and environmental measures to limit exposure to dangerous agents that could affect human health. This is crucial in settings such as healthcare facilities, laboratories, and manufacturing plants, where contaminants can easily spread if not properly managed.
How Does Contaminant Control Work?
Contaminant control works by implementing a combination of personal protective equipment, proper hygiene practices, and environmental controls to minimize the presence and spread of hazardous substances. PPE like gloves, masks, gowns, and face shields act as physical barriers between workers and contaminants, while proper sanitation and ventilation help reduce the risk of exposure. In many industries, contaminant control also involves adhering to strict protocols, such as regularly disinfecting surfaces, controlling air filtration, and maintaining sterile environments to protect workers and prevent contamination.
Key Elements of Contaminant Control
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE is the first line of defense in contaminant control. Items like gloves, masks, face shields, gowns, and respirators are used to protect workers from coming into direct contact with contaminants. Proper use of PPE ensures that contaminants do not enter the body through the skin, respiratory system, or eyes.
- Sanitation Protocols: Effective contaminant control relies on frequent and proper cleaning of equipment, surfaces, and spaces. Disinfectants, sterilization procedures, and proper waste disposal help remove contaminants and reduce their spread in work environments like hospitals and laboratories.
- Ventilation and Filtration Systems: In environments where airborne contaminants are a risk, such as in industrial or healthcare settings, controlling airflow is critical. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters and proper ventilation systems help capture and remove particles, reducing the risk of respiratory exposure.
- Training and Compliance: Ensuring that all personnel are properly trained in contamination control procedures is essential for success. Workers must know how to properly don, doff, and dispose of PPE, as well as how to follow established protocols for sanitation and environmental controls.
Importance of Contaminant Control in the PPE Industry
Contaminant control is a vital part of workplace safety, especially in industries where exposure to infectious agents, toxic chemicals, or other hazardous materials is a concern. By using appropriate PPE and following contaminant control protocols, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of infections, occupational illnesses, and cross-contamination. This is particularly important in healthcare environments, where the spread of infectious diseases can have severe consequences for both patients and medical staff.
In industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and food processing, contaminant control helps ensure product quality by preventing contamination of materials and products. In these environments, controlling contaminants is crucial for meeting regulatory standards and protecting both workers and consumers.
Conclusion
Contaminant control is a fundamental component of occupational safety and health. Through the use of PPE, sanitation protocols, environmental controls, and thorough training, it is possible to effectively manage and limit the spread of hazardous substances. In industries where exposure to biological, chemical, or particulate contaminants is a risk, following best practices in contaminant control is essential for ensuring the safety of workers and maintaining a healthy work environment.
« Back to Glossary Index